Beetroot juice is mostly consumed as part of a healthy diet and has many benefits. But are you aware of the side effects of beetroot juice? For instance, beetroot is high in oxalates, which bind with calcium and may trigger the formation of kidney stones in vulnerable individuals (1).
Accumulation of metal ions in the liver is also associated with excess consumption of beetroot (2).
Fun FactBeetroots are derived from sea beets or wild beets grown on the Mediterranean coast. European immigrants introduced them to Americans.
Does this mean you should completely avoid this nutritious food? No – but having it in moderation and noting the ill effects may help minimize the risk. Continue reading to know further about the side effects of beetroot juice and how you can prevent them.
In This Article
What Are The Side Effects Of Beetroot Juice?
1. Might Cause Beeturia
Beeturia is characterized by the discoloration of urine following the intake of beets or foods colored with beetroots. Urine may range from pink to deep red, and this condition could be prevalent in about 14% of the population and have increased frequency in those with iron deficiency (3).
A study conducted on eight individuals showed that the intake of beetroot juice supplements could lead to beeturia in all but one individual (4).
For the majority, beeturia happens to be a harmless phenomenon that resolves on its own once the individual reduces the intake of beet/beet juice (3).
2. May Increase Kidney Stone Risk

Shutterstock
According to Clinical Nutrition Research, beets are rich in oxalate and may contribute to stone formation (1). If you already have stones, your doctor might recommend you to stop or reduce beetroot/beetroot juice consumption.
There are four types of kidney stones, with calcium being the most common of all. The mineral can combine with other substances, especially oxalate, and form a stone.
Beetroot is high in oxalate and can directly contribute to kidney stones. It increases urinary oxalate excretion, which can lead to the development of calcium oxalate stones (1).
Related: 16 Home Remedies For Kidney Stone Pain And Prevention Tips
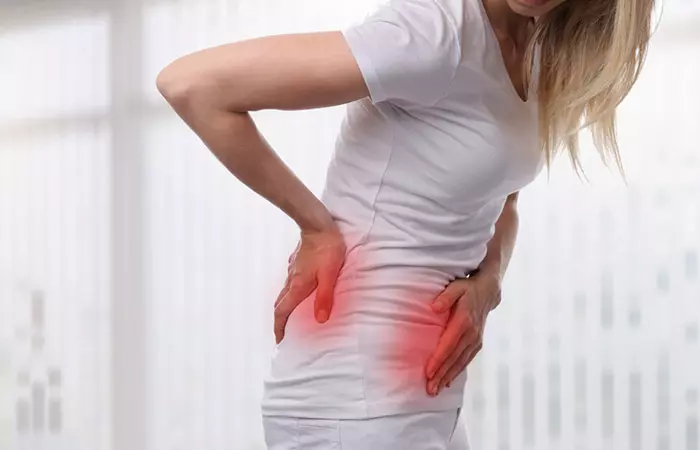
3. May Cause Anaphylaxis

Shutterstock
Though rare, beetroot may cause anaphylaxis, which is an acute allergic reaction to an allergen to which the body has become hypersensitive.
In a study, a young girl complained of urticaria (red rashes on the skin that itch intensely, sometimes leading to dangerous swelling) and asthma after ingesting boiled beetroot (5). The girl also experienced hives, throat tightness, and bronchospasm. She has advised a diet free of beetroot, and she had no symptoms again (5).
4. May Cause Colored Stools
Beetroot (and foods with red coloring) may cause stools to appear reddish (6).
There is some evidence that beetroot may also cause black and tarry stools due to the presence of altered blood (7).
Dark and tarry stools could also be a symptom of beeturia. You may want to visit your doctor and discuss your recent dietary choices and history of similar events (3).
StyleCraze TriviaDuring ancient Greek and Roman times, beets were either white or black and were called Roman beets.
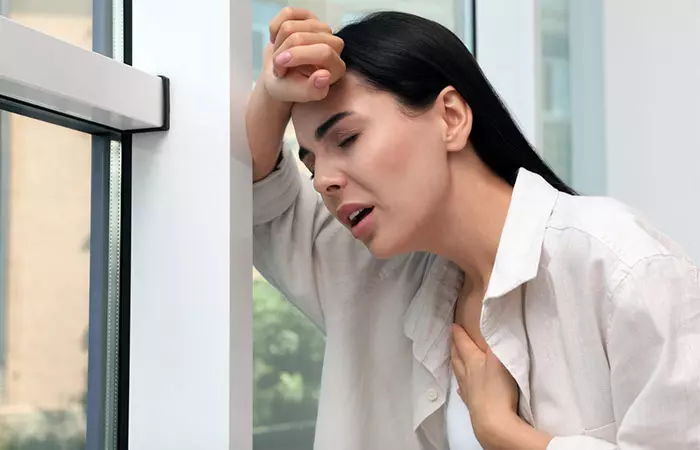
5. May Cause A Stomach Upset

Shutterstock
Beetroot contains nitrates*. According to a publication by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, exposure to high levels of nitrates may lead to abdominal cramps (8).
The juice may also cause stomach problems in some people (9).
*Beetroot and certain other foods contain nitrates, which are converted to nitrites upon ingestion.
Related: Is Pineapple Effective For Upset Stomach?
6. May Cause Problems During Pregnancy

Shutterstock
The nitrates in beets may cause a problem here. Pregnant women are more sensitive to the effects of nitrate. This can be attributed to the natural increase of methemoglobin levels in the blood during the later stage of pregnancy.
Excess nitrate can lead to methemoglobinemia (elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood), causing symptoms like lack of energy, headache, dizziness, blue-gray coloration of skin around the eyes, mouth, lips, hands, and feet (10).
Though most epidemiological studies of pregnant women having elevated nitrate levels in their groundwater did not show any negative effects on their offspring, one study found an association between dietary nitrates and an increase in neural tube defects (10).
7. Might Harm The Liver
Studies suppose that extreme intake of table beetroot may cause several disturbances not only in healthy patients but also in those dealing with metal-accumulating diseases (2).
Excess intake of the veggie can cause the accumulation of metal ions in the liver (2).
Related: Cirrhosis Of The Liver: Causes, Signs, Stages, & Treatments
How Much Of Beetroot Juice Is Too Much?
There are limited research and no official recommendation regarding the safe dosage of beetroot juice. Hence, it is best to consult with your doctor.
Fun FactDuring the mid-19th century, beetroot juice was used to add color to wines.
A Note On SuperBeets
Subscribe 
Shutterstock
SuperBeets is a popular health supplement that allegedly lowers blood pressure and improves circulation. It is made of beetroots that are dehydrated into crystals.
There only is one study about SuperBeets, and concrete evidence on its efficacy to lower blood pressure is lacking. The supplement may lower blood pressure levels, but more research is warranted (11).
Most testimonials from people state that the supplement can lower blood pressure levels. However, certain others reported no benefits. Exact information on SuperBeets is lacking.
If you are vulnerable to the side effects of beetroot juice, the supplement could do more harm than good. Hence, it is imperative to discuss this with your doctor.
Infographic: How To Reduce The Risk Of Kidney Stones
Beetroots are packed with oxalates which if accumulated in the body lead to the formation of kidney stones. This condition, however, can be prevented by incorporating a few lifestyle changes. These are dietary changes that should be strictly adhered to in order to see results.
Check out the infographic below to discover the different ways you can follow to reduce the risk of kidney stones and what foods you should avoid.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Beets are root vegetables with exceptional nutritional values. They are lauded for their many health benefits. However, excess intake of beetroot juice may cause side effects. It may cause discoloration of urine, increase kidney stone risk, lead to anaphylaxis, colored stools, upset stomach, and problems during pregnancy like dizziness and lack of energy. Since no proper dosage is recommended, check your portions while consuming. Consult your doctor if you have any medical condition, like kidney stones, before including beets in your diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should you drink beetroot juice?
The best time to have beetroot juice is early in the morning or 30 minutes before breakfast.
Is it OK to drink beet juice every day?
Yes, you can consume a cup of beetroot juice every day.
Is it good to drink beetroot juice on an empty stomach?
Yes, consuming beetroot juice on an empty stomach helps in better absorption of its nutrients.
Does beetroot juice increase weight?
No, beetroot juice does not increase weight. It is very low in calories and helps in weight loss.
Does beetroot juice cause gas?
Yes, beetroot juice may cause gas and bloating in people with gastrointestinal issues. Hence, caution is advised while consuming it.
Sources
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Check out our editorial policy for further details.
- Nutritional Management of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis), Clinical Nutrition Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4525130/ - Extreme consumption of Beta vulgaris var. Rubra can cause metal ion accumulation in the liver, Acta Biological Hungarica, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17899785 - Beeturia, National Center for Biotechnology Information.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537012/ - Plasma nitrate and nitrite are increased by a high nitrate supplement, but not by high nitrate foods in older adults, Nutrition Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3319660/ - Anaphylaxis to beetroot (Beta vulgaris): a case report, Clinical and Translational Allergy, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3354182/ - Black or tarry stools, US National Library of Medicine.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003130.htm - What color-Mari are your stools?, BMJ, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1255795/ - ToxGuideTM for Nitrate (NO3-) CAS# 14797-55-8 and Nitrite (NO2-) CAS# 14797-65-0, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=FB74D6005F52552224C7CA32C5F3E06E?doi=10.1.1.731.7221&rep=rep1&type=pdf - EFFECTS OF BEETROOT JUICE, PROTEIN SUPPLEMENTATION, AND
RESISTANCE TRAINING ON STRENGTH IN OLDER ADULTS, Wake Forest University Graduate School of Arts and Sciences.
https://wakespace.lib.wfu.edu/bitstream/handle/10339/57158/Tweedie_wfu_0248M_10734.pdf - Methaemoglobinemia in areas with high nitrate concentration in drinking water, ResearchGate
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12482112_Methaemoglobinemia_in_areas_with_high_nitrate_concentration_in_drinking_water - Inorganic nitrate supplementation attenuates peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity but does not improve cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in older adults, American Journal of Physiology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6048463/
Was this article helpful?
Related
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author

Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Ravi Teja Tadimalla is an editor and a published author. He has been in the digital media field for over… more
Ariana Fiorita
(RDN)Ariana is a Registered Dietitian specializing in functional medicine and sports nutrition in the Cleveland, Ohio area. She holds a… more



 23 Amazing Benefits Of Mulberries (Shahtoot) For Skin, Hair, And Health
23 Amazing Benefits Of Mulberries (Shahtoot) For Skin, Hair, And Health 22 Best Benefits Of Oatmeal For Skin, Hair, And Health
22 Best Benefits Of Oatmeal For Skin, Hair, And Health 21 Amazing Benefits Of Litchis (Lychees) For Skin, Hair, And Health
21 Amazing Benefits Of Litchis (Lychees) For Skin, Hair, And Health 10 Nutritional Benefits Of Carrot Juice For Skin, Vision, And Health
10 Nutritional Benefits Of Carrot Juice For Skin, Vision, And Health Honey For Oily Skin – 12 Best Ways To Use It Effectively
Honey For Oily Skin – 12 Best Ways To Use It Effectively Flax Seeds Benefits & DIY Face Masks For Beautiful Skin
Flax Seeds Benefits & DIY Face Masks For Beautiful Skin Parsley: 10 Potential Benefits And Uses, Nutrition, How To Make Tea
Parsley: 10 Potential Benefits And Uses, Nutrition, How To Make Tea 33 Wonderful Benefits Of Banana For Skin, Hair, And Health
33 Wonderful Benefits Of Banana For Skin, Hair, And Health Tea Tree Oil For Warts: Benefits, How To Use, And More
Tea Tree Oil For Warts: Benefits, How To Use, And More