Dopamine is a feel-good hormone that plays a key role in your brain health. It acts as a neurotransmitter (a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells). Certain foods can enhance dopamine levels, and the intake of dopamine foods benefits your health in many ways. What is the science behind dopamine? What foods should you include in your diet? This article explores the foods that enhance dopamine levels, the side effects of dopamine excess consumption, and problems you may face with dopamine deficiency. Keep reading.
In This Article
What Role Does Dopamine Play?
Dopamine is released by the dopaminergic neurons located in the midbrain. These neurons, though few in number, play an important role in mood, addiction, reward, and stress (1).
Dopamine also plays a role in learning, working memory, motivation, and decision-making. It controls movement too – and its deficiency may be one of the causes of Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (2).
The anticipation of a reward increases brain dopamine levels. Many addictive drugs also increase its release from the neurons. This is one reason most addicts have a hard time quitting drugs.
Hence, dopamine plays a critical function in brain health. But how can you increase dopamine levels naturally? Well, the best way is to eat foods that boost dopamine levels.
Which Foods Boost Dopamine Levels?
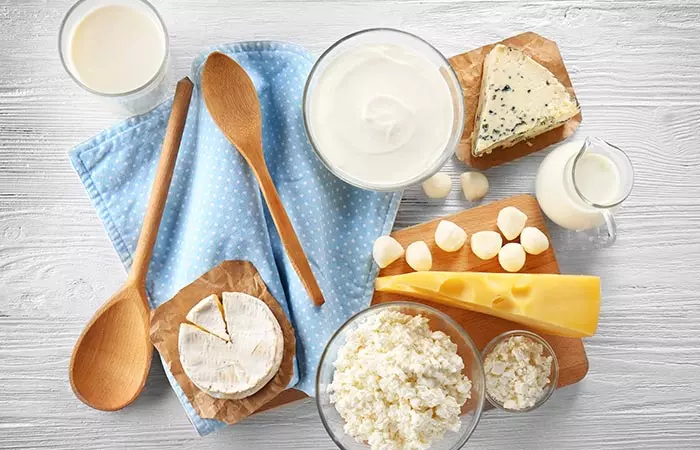
1. Dairy Products

Shutterstock
These include everyday foods like cheese, milk, and yogurt. Cheese contains tyramine, which is converted into dopamine in the human body (3). Foods containing probiotics, like yogurt, also boost dopamine levels (4).
2. Nuts
Nuts rich in vitamin B6 help as this vitamin helps your brain produce dopamine (5). Walnuts and hazelnuts are good sources of vitamin B6. Walnuts also contain DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid, which is responsible for the modulation of dopamine concentrations (6). Walnuts and almonds are good sources of folate, which also helps produce dopamine (7).
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Shutterstock
In rat studies, omega-3 fatty acids were found to normalize dopamine levels and reduce the development of anxiety-like behaviors (8).
In another study, oral fish oil treatment was found to restore dopamine release after traumatic brain injury (9).
Foods rich in omega-3 include fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, and other foods, such as walnuts and chia seeds.
4. Dark Chocolate
Studies show that chocolate may interact with a number of neurotransmitters, including dopamine. Dopamine is released after eating dark chocolate and imparts a pleasurable sensory experience (10).
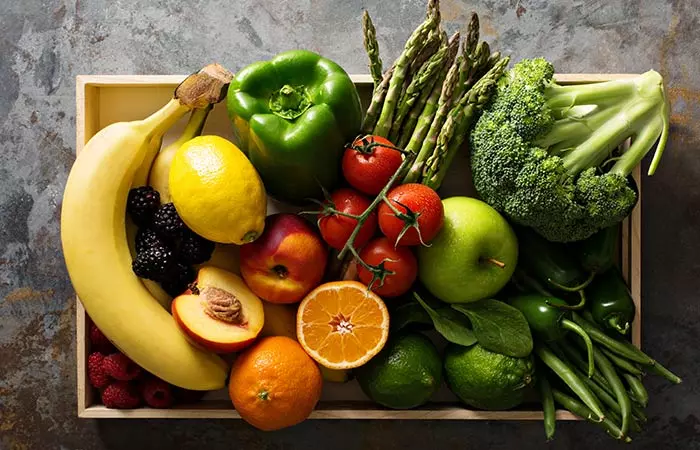
5. Fruits And Vegetables

Shutterstock
In a study, rats supplemented with strawberry and spinach showed a significant enhancement in dopamine release. The study suggests that in addition to the antioxidants, the other nutrients in fruits and veggies may also contribute to dopamine release (11).
Even bananas were found to have high levels of dopamine – more so in the peel and pulp. Avocados and velvet beans also contain dopamine. Other fruits and veggies containing dopamine include oranges, apples, peas, tomatoes, and aubergines (12).
6. Coffee
Like most other wake-promoting drugs, the caffeine in coffee enhances dopamine signaling in the brain (13). Caffeine’s main targets in the brain are the adenosine (a brain chemical that dampens brain activity) receptors. It works on these receptors and sets off a chain of events, which eventually affects dopamine levels and lights up the areas of the brain associated with pleasure and thinking (14).
These are the top foods that can boost your dopamine levels. But hold on – is there anything like too much dopamine?
What Are The Effects Of Excess Dopamine?
Excess dopamine levels in the system can lead to paranoia and withdrawal from social situations. They can even lead to overly intense and impulsive behaviors.
Dopamine also plays a role in inhibiting prolactin (a hormone) secretion by the pituitary gland – which may otherwise cause menstrual disorders and infertility (15). Excess dopamine may not be able to effectively inhibit prolactin, leading to these issues.
But worry not – dopamine overdose is likely to happen only if you take the hormone intravenously (which is often the case with individuals who are deficient in dopamine).
The normal dopamine ranges are 0 to 30 pg/mL (picograms per milliliter).
What if your dopamine levels go below these ranges? Well, that causes problems too.
What Are The Effects Of Dopamine Deficiency?
Dopamine deficiency is linked to certain mental disorders, though they are not found to cause the condition directly. Some of these mental disorders include Parkinson’s disease, depression, schizophrenia, and psychosis.
Following are the symptoms of dopamine deficiency: (16)
| Physical Issues | Personality Issues | Memory Issues | Attention Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia
Balance problems Blood sugar instability Bone density loss Carbohydrate binges Digestive problems Food cravings High blood pressure Kidney problems Low sex drive Muscle cramps or tremors Obesity Thyroid disorders Trouble swallowing |
Aggression
Anger Depression Hopelessness Inability to handle stress Isolating oneself Mood swings Procrastination Self-destructive thoughts |
Distractibility
Failure to listen and follow instructions Forgetfulness Poor abstract thinking Slow processing speed |
Attention deficit disorder
Decreased alertness Hyperactivity Impulse behavior Poor concentration |
Dopamine is a feel-good hormone that acts as a neurotransmitter. It plays a key role in brain functioning. You can increase dopamine levels naturally by consuming foods rich in the hormone. These foods include dairy products, nuts, omega-3 fats, dark chocolate, fruits and vegetables, and coffee. However, excess dopamine levels may lead to overly intense and impulsive behaviors. Hence, consume it in the recommended dosage levels to avoid adverse reactions.
What do you think about this article? Any suggestions? Do let us know by leaving a comment in the box below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does vitamin D increase dopamine?
No. Nevertheless, vitamin D serves as a protective agent and helps prevent inflammation and oxidative stress that may occur in the dopamine-releasing areas of the brain (17).
Subscribe
Does alcohol release dopamine?
Yes. Alcohol can increase dopamine release even at low doses, which may explain the effect of alcohol dependence in some individuals (18).
Does peanut butter increase dopamine?
Yes. Research has shown that peanut butter acts as a dopamine-rewarding food in mice (19).
Key Takeaways
- Dopamine plays a key role in addiction, mood, your ability to learn, memorize, and make decisions.
- Dairy products, nuts, omega-3 fatty acids, dark chocolates, fruits and vegetables, and coffee can increase dopamine levels.
- Excess dopamine levels may cause paranoia, impulsive behaviors, infertility, and other side effects.
- A deficiency may lead to Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and others.
References
- “Dopaminergic neurons” The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Dopamine: the rewarding years” British Journal of Pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Dopamine formation from tyramine…” Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, US National Library of Medicine.
- “There’s a scientific reason some people are…” The University of Michigan.
- “Effect of vitamin B6 nutrition on the levels…” Neurochemical Research, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Effects of walnut consumption on…” Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine.
- “10 foods that fight stress” Mass Public Health Blog.
- “Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in…” Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Oral fish oil restores striatal dopamine…” Neuroscience Letters, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Mood state effects of chocolate” Journal of Affective Disorders.
- “Effect of fruits, vegetables…” The Journals of Gerontology, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Dietary neurotransmitters…” Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Caffeine increases striatal dopamine…” Translational Psychiatry, US National Library of Medicine.
- “What is it about coffee?” Harvard Medical School.
- “Prolactin and dopamine…” Journal of psychopharmacology, US National Library of Medicine.
- “The Edge Effect: Revolutionary brain-mind-body science”. NutriNews, Braverman, Eric (2005).
- “Vitamin D protects dopaminergic neurons against neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in hemiparkinsonian rats”. Journal of Neuroinflammation.
- “Alcohol and Dopamine”. Alcohol Health Res World.
- “Ghrelin increases intake of rewarding food in rodents”. Addiction Biology.
Related
The following two tabs change content below.
- Author
- Reviewer

Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Ravi Teja Tadimalla is an editor and a published author. He has been in the digital media field for over… more
Elisa Olivier-Nielsen
(MA, RDN)Situated in Northern Arizona, Elisa Olivier-Nielsen’s private practice offers both in-office and virtual consultations nationwide. As a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist… more



 29 Amazing Benefits Of Figs For Skin, Hair And Health
29 Amazing Benefits Of Figs For Skin, Hair And Health 19 Amazing Benefits Of Black Chickpeas (Kala Chana) For Skin, Hair And Health
19 Amazing Benefits Of Black Chickpeas (Kala Chana) For Skin, Hair And Health 28 Best Shea Butter Benefits For Skin, Hair And Health
28 Best Shea Butter Benefits For Skin, Hair And Health 15 Best Benefits Of Beta Carotene For Skin, Hair And Health
15 Best Benefits Of Beta Carotene For Skin, Hair And Health 29 Amazing Benefits Of Sesame Seeds For Skin And Health
29 Amazing Benefits Of Sesame Seeds For Skin And Health 4 Reasons Goat Cheese Is Better Than Cow Cheese
4 Reasons Goat Cheese Is Better Than Cow Cheese 38 Benefits Of Lime For Skin, Hair, And Health + Nutrition
38 Benefits Of Lime For Skin, Hair, And Health + Nutrition Rice Water For Skin – How To Use It For Maximum Benefits
Rice Water For Skin – How To Use It For Maximum Benefits 9 Benefits Of Cranberry Tea For Health And Recipes To Try
9 Benefits Of Cranberry Tea For Health And Recipes To Try